Personal Income Tax
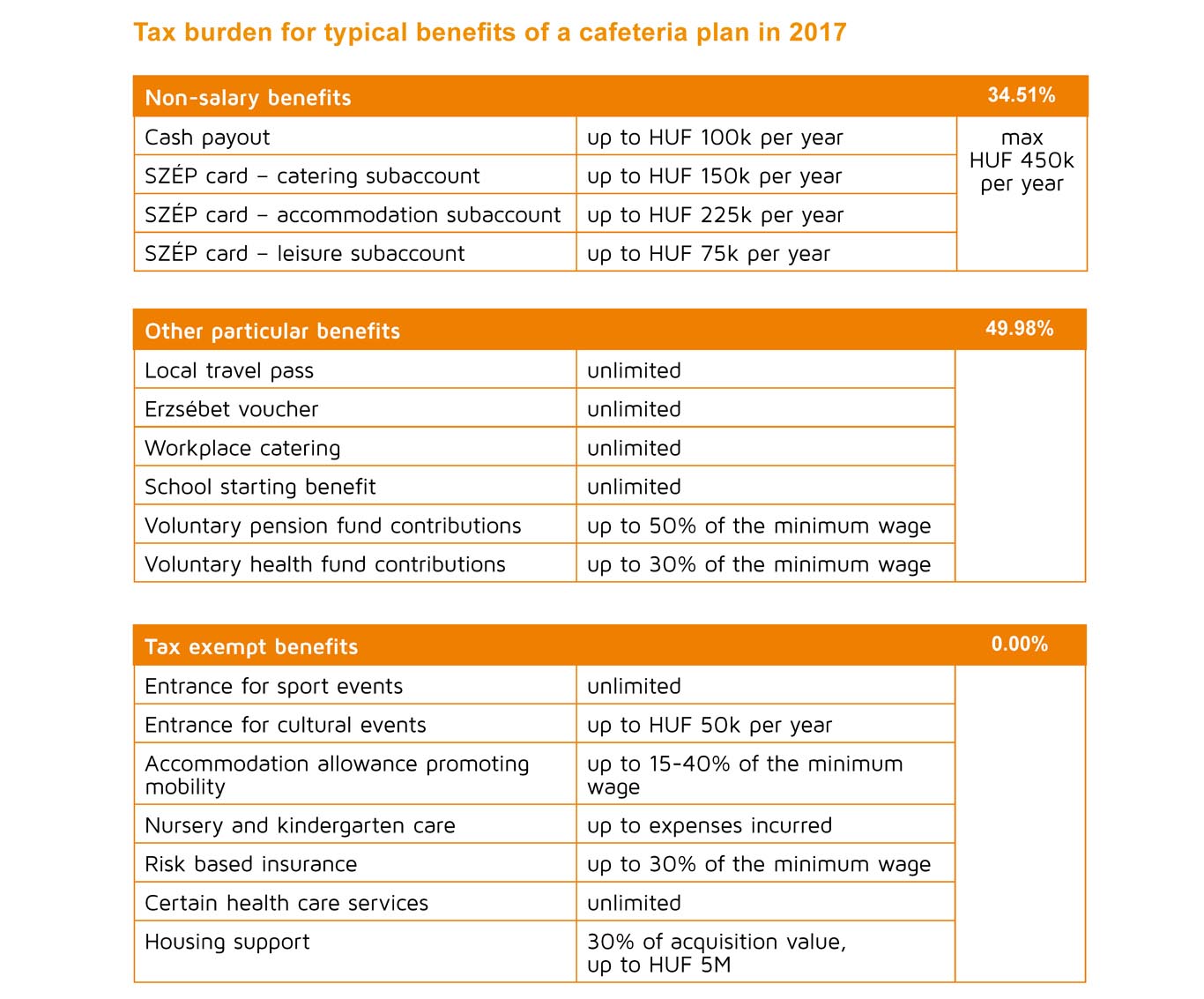
Non-salary benefits
Several well known and popular non-salary benefit elements will be phased out, including the Erzsébet voucher, school starting benefit, local travel pass, cost of education provided within the school system, voluntary health and pension fund contribution. Starting from 1 January 2017 these benefits will be subject to a higher tax burden of 49.98% (as opposed to the current 34.51%). Practically, of all the non-salary benefits it is only the SZÉP card which is going to retain its preferential tax status. The amount distributable under the SZÉP card scheme also remains unchanged. In lieu of the terminated non-salary benefits the employer will be able to allot cash payouts capped in the annual amount of HUF 100k with a tax burden of 34.51%. Total financial envelope available under preferential tax treatment in a given year will be maximized in HUF 450k that can be provided in a SZÉP card exclusively or combined with the HUF 100k cash payout. In case the employment does not take up a whole year the cap shall be considered proportionally.
From next year, new tax exempt benefits will be introduced. One of the new elements is the accommodation allowance to promote the mobility of employees. Once the necessary conditions are fulfilled the flat rental fee can be supported free of tax with an amount up to
- 40% of the minimum wage during the first 24 months of employment
- 25% of the minimum wage during the second 24 months of employment
- 15% of the minimum wage during the following 12 months thereafter.
Certain health care instruments provided by the employer will also be available free of tax. As of 1 January 2017 kindergarten care as non-cash benefit can also provided exempt of tax.
Commutation expense reimbursement
In the absence of adequately accessible public transportation employers will be able to reimburse employees who use their cars for commuting up to the amount of HUF 15 per km from next year without any tax burden (the current cap is HUF 9 per km).
Click on the picture to enlarge it.
The tables are also available as a part of pdf of Process Solutions Newsletter here.
The definition of secondment
Secondment is currently defined as a placement of the employee to render work on a location other than the principal place of work defined in his work contract. As of 1 August 2016 the definition will change and secondment will be specified as business travel ordered by the employer with the exception of commutation.
Equity increase from undistributed profits
The new Civil Code allows the increase of share capital from undistributed profits, but so far this has been regarded as a source of other income for the individual owning the business. As per the amendments, this form of equity increase will cease to constitute revenue at the individual; however, the company will have to report the transaction to the Tax Office. The changes will be effective as of 1 August 2016 but will already be applicable for the determination of 2016 tax liability.
Social Security Contributions
Secondment in Hungary
The exemption (of social security charges) available for 3rd country citizens working in Hungary in the form of secondment, assignment or temporary agency employment will be extended also to those 3rd country citizens, whose country of citizenship does not have a social security treaty in place with Hungary, or the individual itself is not subject to the EU regulations on the coordination and implementation of social security systems. This extended exemption can already be applied for secondments commencing in 2016.
Under current regulations such secondments with a duration exceeding the standard two years limit are also eligible for exemption of social security liabilities for their entire period, provided the prolongation beyond the default 2 year period is necessitated by unforeseen circumstances and moreover, this fact has been duly reported to the Tax Office. This option will be eliminated as of 1 January 2017, meaning that the individual will be subject to social security liabilities as of the ending of the first two years of the secondment even if the prolongation is reported to the Tax Office. Failure in reporting the prolongation within 8 days will trigger a social security liability retroactively, for the entire duration of the secondment. According to transitory rules prolongations reported until the year end of 2016 are only warrant exemptions up to 30 June 2017 at the most.
Social Contribution Tax
Regulations on Secondment
The above discussed changes in social security regulations regarding the secondment of 3rd country citizens necessitated an update in the context of social contribution tax as well.
As for secondments started after 1 January 2016 the scope of seconded employees eligible for exemption expands in tandem with the one described under social security regulations.
However in respect of the prolongment of secondments there is a discrepancy between the social security and social contribution tax regulations: rather than granting exemption, the prolongation triggers social contribution tax liability retroactively, going back as far as the starting date of the secondment.
As of 1 January 2017 the regulations will be eased and reconciled with the ones of social security: in case of prolongment, the social contribution tax liability will only kick in after the 2nd year of secondment.
Tax allowances
Career Bridge allowance
The allowance will be re-introduced as of 1 August 2016. This allowance had previously been available for the employment of former public sector employees leaving their position due to downsizing.
A certification issued by the former public sector employer until 31 August 2017 is required in order to make use of the allowance. The allowance is available for a period of 12 months, in the amount of 13.5% of the gross salary (latter capped at twice the amount of the minimum wage).
Research and development allowance
Employers arriving to a negative corporate income tax base on account of the tax base adjustments due to the direct costs of R&D activities of their own are also eligible for social contribution tax allowance. The amount of the allowance is calculated as 19% on the half of the negative tax base.
Other allowance related regulations
There has been a conceptual clarification in relation to the allowance available for hiring the permanently unemployed – it has been made unambiguous that the time spent in public employment shall also be considered when determining the eligibility for this type of allowance.
For allowances available for the employment of permanently unemployed and career starters below the age of 25 it has also been ascertained that in the event of a change of employer eligibility will not be revoked.
According to the general rule pertaining to all the allowances, in the event of parallel employments a given allowance cannot be claimed multiple times. Moreover, if the same employer and employee re-enters in an employment contract, there is no way to claim the same allowance a second time around.
Value Added Tax
Goods and services under reduced rate
As of 1 January 2017 some basic food products (chicken meat, eggs, fresh milk) are going to be subject of the 5% reduced rate. The provision of internet service and restaurant service will be taxed with a rate of 18%. The rate applicable for restaurant service will be decreased further to 5% as of 1 January 2018.
Requirements regarding the content of invoices
From next year the first 8 digit of the customer’s VAT identification number will have to be included on the invoice also in domestic relation if the amount of the output tax equals or exceeds HUF 100k (the current limit is HUF 1M). This is necessitated by the extended data content required by the domestic VAT summary report as of 1 July 2017.
Reverse charge
Starting from next year reverse charge mechanism shall be applied also to those construction services which are not subject to prior authorization and only required to be reported to the competent authorities.
Tourism development contribution
New tax from 2018
As of 1 January 2018 a new tax will be introduced on restaurant services. The ‘tourism development contribution’ will be levied on the net revenues derived from such services at a rate of 4%.
Stamp duty
We would like to point out as a reminder that — as already mentioned in our previous newsletter — the acquisition of buses, trailers and trucks will be exempt of stamp duty as of 16 June 2016.
The calculation method to be applied when determining the equity participation rate in a company holding domestic real estate assets has been updated. As of 1 January 2017 the shares held by individuals should also be factored in. This is of paramount significance when determining if the transaction is subject to stamp duty liability in the event of acquiring shares in such company (stamp duty liability sets in at a participation rate of 75%).
As of 16 June 2016 the certificates proving the fulfilment of tax, stamp duty and social security obligations will be exempt of stamp duty.
Advertisement Tax
The changes in advertisement tax threatens with a crackdown on those global corporations (Google, Facebook) which the government is determined to tax despite the fact that they are not established within the territory of Hungary.
Company car tax
As of 1 January 2017 company car tax liability for passenger cars financed via operating lease will be shifted to the lessor (we have seen all this before). Passenger cars leased out for individuals will also be subject to tax provided for such cars only depreciation is accounted for.
Rules of Taxation
Limitation period for collection of tax debt
In the event of a court judgement affecting the taxpayer’s tax liabilities beyond the statute of limitation the taxpayer will be entitled to revise its tax returns also for the said tax periods beyond limitation in order to be able to settle its tax liability. The Tax Office will have one year from the date of filing to audit the revised figures. If the judgement pertains to a period already closed by a tax audit the Tax Office will redo the audit by the request of the taxpayer, thus enabling the taxpayer to settle its obligation. The new regulations will be effective as of 1 July 2016.
Although the period available for the Tax Office to assess taxes remains 5 years as before, cutting back the statue of limitations period for collection of tax debt is certainly a welcome change for taxpayers. The 4 year is to be counted from the last day of the calendar year in which the tax was originally due. The new regulation will be effective as of 1 July 2016.
EKÁER – Electronic Trade and Transport Control System
The transport of non-risky goods with vehicles not subject to road toll payment will also have to be registered under the EKÁER system if the gross weight of the vehicle exceeds 3.5 tons after loading.
Overreporting the quantity of actually transported goods in the EKÁER will also be penalized in the future. The 40% default penalty will be levied on the difference between the reported and the actually transported value of the goods.
The changes will be effective as of 1 August 2016.
Underlying liability
Pursuant to a modification effective as of 1 September 2016 the limited nature of the shareholders’ liability will be possible to circumvent in tax affairs i.e. under certain conditions the ‘company veil’ (granting immunity from personal liability) can be pierced and shareholders disposing of their shares can be compelled to vouch for the tax debt incurred by the company. The former shareholder of the company can be made liable for the tax debt in proportion of his former participation in the company.
The underlying liability can only be evoked in case of the shareholder’s wilful misconduct provided the former shareholder controlled at least 25% of the voting rights and the net tax debt of the company exceeds 50% of the company’s equity at the time of the share sale. Grounds of excuse based around the member’s acting in good faith will be restricted substantially as of 1 August 2016.
The shareholder will only be acquitted of his underlying personal liability if the company’s tax debt remained outstanding on account of unsettled customer receivables and moreover, the company has taken adequate measures to collect its outstanding receivables, to make up for its equity shortage, and to settle its tax debt.
Changes pertaining to reliable and risky taxpayers
According to a change of which all taxpayers are going to be benefit, the rating of taxpayers will be based upon the net tax debt for the future.
Pursuant to further amendments, an entity will be identified as risky taxpayer if it is currently subject to compulsory cancellation procedure amount of net tax debt due from the entity in the current year and in the 5 years preceding the current year exceeds 70% of total taxes due for the current year the amount of default penalty levied on the entity that become due in the two years preceding the current year exceeds 70% of total taxes due for the current year
The above guidelines will be effective as of 1 July 2016 and will first be applied for evaluation periods following Q3 2016.
Cancellation of Tax Number
Pursuant to the amendments the failure to register the company’s representative with the Tax Office will not result automatically in the cancellation of the company’s tax number. The Tax Office will be required to call upon the company to remedy such default before taking any invasive actions.
A cancelled tax number will only be replaced once the reasons leading up to the cancellation have been addressed by the taxpayer.
As of 16 June 2016 the rules on the cancellation of tax number due to the non-returning of ’KOCKERD’ questionnaire to the Tax Office have also become more lenient. According to the new regulation the cancellation process — initiated in response to the taxpayer’s failure to return the KOCKERD in due time — will have to be aborted once the submission is made.
Binding rulings
In the future requests for advance tax ruling will have to be submitted to the Tax Office with a written professional opinion from the Chamber of Hungarian Auditors attached.
A new form of tax audit focusing on binding tax rulings will also be introduced. In the course of these audits the Tax Office will test the manifestation of business case outlined in the ruling request in reality.
On-line billing, domestic VAT summary report
Invoices with a VAT content of as low as HUF 100k will have to be included in the domestic VAT summary report as of 1 July 2017 (the current threshold is HUF 1M).
Furthermore, according to plans data will have to be reported by some electronic means about invoices which are generated in an invoicing software (at this point details are still work in progress).
Corporate income tax
Obtaining tax advantage
If the main motive behind a transaction is to obtain tax advantage then the expenses incurred in relation with such transaction will be deemed non-deductable and the tax advantage (tax exemption or benefit) itself that the company aimed to gain will not be permitted to be invoked. This represents a fundamental change in the approach of the regulation as previously only transactions with the sole purpose of tax evasion were deemed illegitimate.
Royalty related tax allowances
Opportunities to make use of royalty related tax allowances are going to be reduced as of 16 July 2016. On one hand by changing the definition of royalty commercial and marketing related rights like trademarks and brand names have been banished from the concept thus in the future the application of tax allowances will be restricted to rights and know-hows associated with production and software.
Furthermore, profit before tax will be allowed to be reduced by 50% of the profit earned on a royalty transaction as opposed to the current practice where 50% of the income can be accounted for as allowance.
Previously acquired intangibles conferring entitlement to royalty will remain subject to current rules.
Pursuant to a further change 50% of the loss made on the sale of intangibles conferring entitlement to royalty will become a tax base increasing item provided that in the preceding tax year the tax base was decreased with respect of profits made on the same intangible.
Preferential business transformation and transfer of assets
The conditions set for preferential business transformation and preferential transfer of assets have been supplemented with a new one: the transaction has to be based on valid economic or commercial reasons and it is for the taxpayer to prove the existence of such underlying reasons.
Promoting employees’ mobility
Expenses incurred in relation to the accommodation allowance promoting the mobility of employees or to the creation and maintenance of workers’ hostels will constitute tax base decreasing items.
Other tax base decreasing items
The maintenance cost of buildings classified as historical monuments – on top of being tax deductive – will also be eligible to reduce the tax base up to 50% of the pre-tax profits.
Renovation expenses of historical buildings will be eligible for a threefold deduction and what is more, they also qualify as tax base decreasing item twice of their amount. Moreover there will be no upper limit on reducing the tax base this way, meaning that the deductions are allowed to push the tax base to the red.
In the future the 20% amount of intercompany receivables which are overdue for more than 365 days can only be utilised to decrease the tax base if the taxpayer also provides data about the particulars of the related party and the reasons behind the irrecoverability of the receivable.
Tax base increasing items
Foundations, associations and public bodies will have to add back their costs incurred in relation with the utilisation of property to their tax base even if they do not perform business activities at all.
In case of preferential transfer of assets, the transferring company has to increase its tax base with the amount of tax deduction it had claimed earlier in relation with the asset transfer if the participation received in exchange for its assets is disposed of before the deferred corporate tax is paid.
Loss carry forward
50% of the negative tax base incurred due to the application of R&D tax deductions will be allowed to carry forward but only if the company has also claimed for social security tax allowance in respect of its R&D activity.
Transfer pricing
As of 2018 the reduction of tax base on account of transfer prices exceeding the arms length price will only be allowed if the related party also performs the corresponding adjustment i.e. increases its tax base. Currently there is no such pre-condition; a statement confirming the amount of tax adjustment is the only thing that is presently required from the other party.
Transactions involving a foreign company and its Hungarian branch will have to be documented only if those transactions are taxable in Hungary (according to the double tax treaty in place).
Progressive exemption
When calculating the tax liability of a parent company which has also tax exempt profits from abroad, an average tax rate shall be applied. This average tax rate is to be determined on the combined amount of profits earned both in Hungary (by the parent) and abroad (by foreign branches or permanent establishments in abroad).
Business expenses
Transactions without consideration will have to conform to stricter rules to be recognized as business expenses. As of 2017 upon filing its tax return the party on the receiving end will have to issue also a statement declaring that the corporate tax have been paid on the income resulting from the said transaction.
Expenses incurred by workplace nurseries will be recognized as business expense in the future.
Support for spectator sports
A company supporting spectator sports will be allowed to accept consideration in exchange for its donation only up to the amount of the ’additional sport development support’. Displaying the name of the supporter is not regarded as consideration.
Local Taxes
Local Business Tax
The changes introduced to the definition of licence fee under the Act on Corporate Income Tax have mostly been mirrored also under the Act on Local Taxes, except that the base of local business tax will be allowed to be reduced by the income deriving from a licence fee transaction, as before (under Corporate Income Tax it is the profit that will be eligible for the 50% tax allowance).
Pursuant to a previous amendment businesses will be allowed to file their local business tax returns also with the Tax Office which in turn will forward their returns to the competent municipalities. This regulation has been supplemented with the option to make use of the mediation of the Tax Office also in respect of revised tax filings. The catch is, though, that the Tax Office will only forward returns which are filed electronically.
Building tax and land tax
Foundations will only be exempted from building tax and land tax if they are registered as owners of such property in the land registry and the property is utilised in close connection with their main activity. As further condition, the Tax Office shall also be notified of this fact in writing annually by the end of each May.
To avoid abuses with regard to the tax exemption of urban properties with an area of less than 1 hectare under agricultural use, the requirements to be fulfilled for the tax exemption of such properties will be tightened.
Other taxes
Small business tax (KIVA)
Headcount limit set as a criteria for the availability of KIVA tax scheme has been increased to a maximum of 50 employee (from the current number of 25). As a consequence the upper headcount limit over which a taxable person under KIVA will be compelled to abandon this tax scheme has been elevated to 100 (from the current limit of 50).